What does 'good food' mean?
This piece is part of the the Good Food Insights series, a collaboration with FamilyFarmed and Esca Bona, which unpacks the dynamics driving the good food movement.

Any serious industry watcher would agree that the good food movement has had a major impact on how consumers view and buy food. Yet numerous interpretations of what exactly good food is exist.
Definitions crafted by thought leaders have many similarities, but with differences in focus and intent. For example, the Center for Good Food Purchasing puts a heavy emphasis on fair labor practices. The Michigan Good Food Charter places an intense focus on food access and better food in schools.
Industry data analysts such as SPINS go more granular. The company tracks retail sales data and uses multiple layers of criteria to ascribe which individual consumer packaged goods (CPGs) are considered natural, organic and specialty products, which is yet another way of defining good food. By its figures, the sector has nearly doubled over just the past eight years, from $68 billion in 2010 to an estimated $134 billion in 2018.
FamilyFarmed—our advocacy nonprofit in Chicago—works to bring all these perspectives together into an aligned definition of good food. Our starting definition was this: Good food is food produced as locally as possible using sustainable, humane and fair practices.
Three years ago, we empaneled a Good Food Commission (presented in the downloadable PDF below) composed of more than two dozen experts—academics and practitioners—from across the food issues spectrum. What followed were two years of discussions and deliberations, including two commission working sessions at SPINS offices in downtown Chicago.
The commissioners and staff relied heavily on scientific research, reports and studies to draw conclusions about the characteristics of good food products. A category of food, e.g. processed or ruminants, was evaluated under four areas of health using the best available science.
For example, with GMOs, we looked at what studies show about how they affect human health, but very little could prove a negative impact. Environmentally, however, stronger evidence exists that GMOs have a negative effect.
Soil was also a much-discussed topic. There is a significant body of recent science about how soil maintenance affects human and environmental health, prompted first by the organic agriculture movement, which spurred the creation of federal organic standards (and the USDA Organic label), and more recently by advocates of regenerative agriculture, which focuses on improving and restoring soil health while sequestering carbon to reduce global warming.
Farming practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation and adaptive grazing methods have shown dramatic increases in sequestered carbon and water retention—not to mention that the increased biodiversity of microorganisms increases positive impacts on the human body.
These conversations produced a framework of a good food definition that focuses on four common themes that encompass areas of “health.” These are human health, environmental health, economic health and social health. The accompanying chart shows how the commission sees the emphases and nuances of the existing definitions—from the Center for Good Food Purchasing, the Michigan Good Food Charter, the Barilla Foundation, the Lexicon of Food and HowGood—fitting within the grid of these health categories.
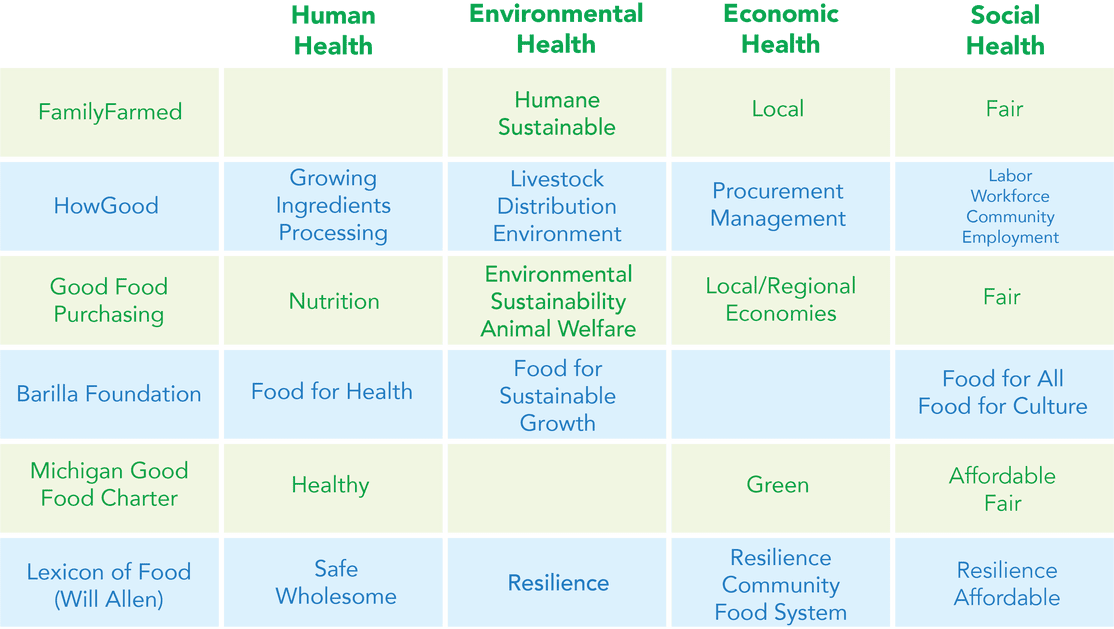
The complexity of the food system presents serious challenges in defining when a food item possesses human, environmental, economic and social consequences. The area of processed foods, aka CPGs, is a particular minefield. For example, most major breakfast cereal manufacturers added whole grains to their products, with some also reducing sugar. Do the changes make these products truly healthy, or are they still too light on nutrition and too heavy on sugar? As you would expect, this is often a very tough call.
As Anubhav Goel, SPINS’ president of client growth solutions, notes, “Many CPGs begin by taking the ‘bad stuff’ out, then they strive to put ‘good ingredients’ in. In contrast,” Goel notes, “new brands start from scratch, so they often create a product that meets more of the criteria for good food.”
FamilyFarmed is proud to partner with New Hope Network on this series of articles that will unpack the dynamics driving good food. In coming months this series will feature portraits of the national good food landscape and individual industry sectors, and we will continue to back those insights up with facts provided through our partnership with SPINS.
For our next article, we’ll take a look at good food consumers—who they are and what motivates them to seek and migrate toward good food. Your feedback is welcome.
For a complete look at the definitions of good food, click "download" below.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like




